
During respiration, mitochondria use oxygen and produce carbon dioxide. MitochondriaĪmong the most prominent organelles of a cell are the mitochondria. It provides a pipeline between the nucleus and cytoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum membrane connects the lumen to the cytoplasm. A cell’s nucleus is made up of different layers that play a role in processes like the production of protein and the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates. Endoplasmic ReticulumĮukaryotic cells possess a network of membranes. Throughout the cytoplasm, such organisms will carry out informational and administrative functions. One-celled bacteria and cyanobacteria have no nucleus and are prokaryotes. Most cells have one nucleus, but slime moulds and siphonal algae are exceptions. Within the nucleus envelope, most of the nucleus contains chromatin that condenses down to chromosomes as a cell divides. NucleusĪ nucleus has three parts: an outer nuclear envelope, chromatin and nucleolus. Its many components are proteins, mRNA, ribosomes, sugars, ions, amino acids, messenger molecules, etc. Proteins, organelles, and other cell structures float in the cytosol, a water-based solution found inside the cells. Moreover, the cytoplasm is cytosol, allowing organelles and substances to move around the cell. Organelles or nucleus do not occupy an animal cell’s private portion. It can control how many substances enter and leave the cell. Selectively permeable materials only allow certain molecules to pass through. Plants and animals have evolved from eukaryotic cells, sharing certain organelles.Įven though plant cells are eukaryotic, the difference between animal cells and plant cells can easily be identified by the presence of chloroplasts in them.Ĭellular movement is controlled and regulated by the plasma membrane. The absence of cell walls result in an irregular shape. The irregular shape of the cell is another defining characteristic. If you study the Structure of an animal cell, you will notice that the cells of animals are generally smaller than those of plants. A microscope is necessary to view most animal and plant cells since their diameters typically range between 1 and 100 micrometres. A single-celled organism, which gave rise to Animalia, lost this characteristic in the distant past.
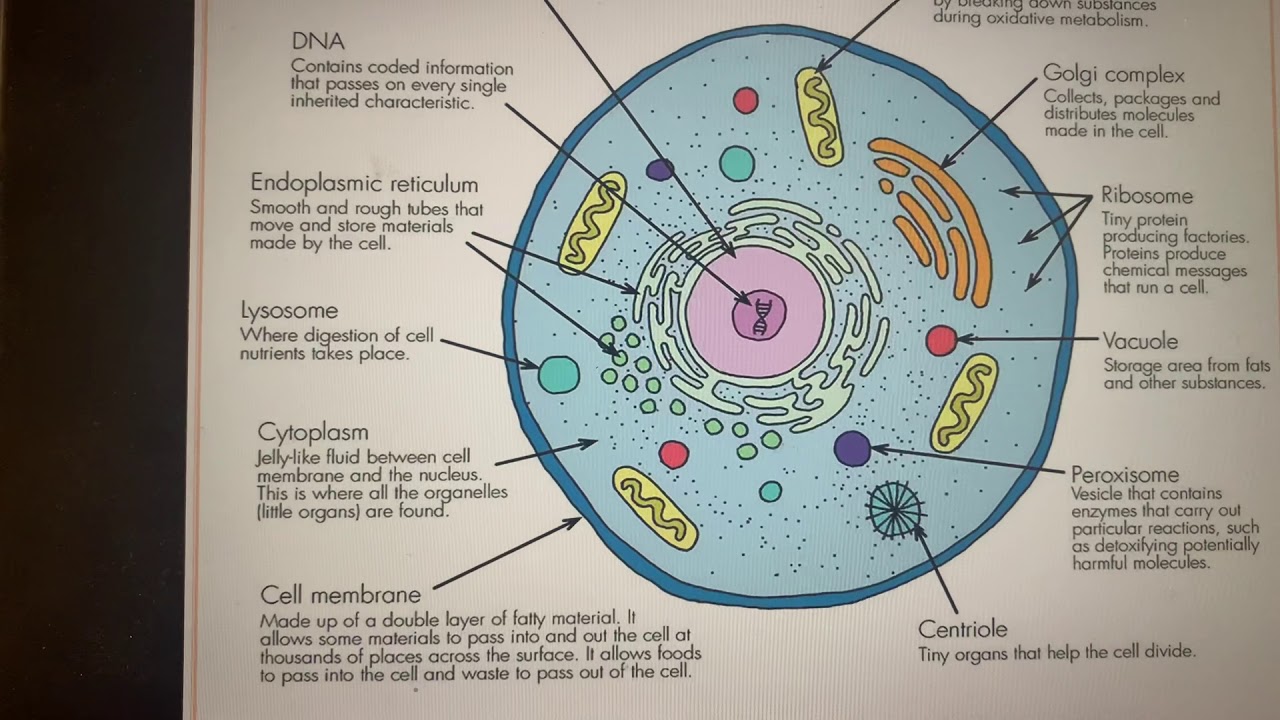
Plants and fungi have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Typical eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane and contain organelles and nuclei bound to the membrane. The structure of an Animal cell consists of many things like Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, and all have their own functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
